mac-monitor is an excellent open-source tool for observing macOS at a low level, but its real value shines when you truly understand the Endpoint Security Framework (ESF) events it surfaces.
Endpoint Security events aren’t just raw notifications – they reveal the inner workings of process creation, file access, network activity, and more. In this guide, we’ll use mac-monitor as our window into ESF to break down the most important event types:
- EXEC and FORK: Process lifecycle events – what they tell you about new processes and their origins
- OPEN, RENAME, UNLINK: File operations and how to spot suspicious modifications
- NETWORK events (when available): Outbound connections and their context
- Authorization decisions: Allow vs. deny, caching, and performance implications
- Event structure deep dive: Paths, PIDs, signatures, responsible auditors, and flags
Through live mac-monitor runs and annotated output, you’ll learn to interpret these events confidently – whether for security research, malware analysis, troubleshooting, or building your own tools.
No prior ESF expertise required – just clone mac-monitor and follow along. By the end, you’ll see macOS system activity in a whole new light.
More information and download is located here:
mac-monitor Event Classes
These are the Event Classes (categories) in mac-monitor‘s graphical interface. When you start a trace/session, the app lets you toggle subscriptions to groups of related Endpoint Security Framework (ESF) events.
This grouping makes it easy for beginners to enable/disable entire categories at once, reducing noise and focusing on specific areas (e.g., turn on only “Process” and “File system” for basic malware hunting). Each class bundles multiple individual ES event types (like ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_EXEC), and mac-monitor enriches them with extra metadata (e.g., code signing certs, paths, quarantine status).
This list provides matches of the current (as of early 2026, v2.1+) organization in the app’s subscription panel – expanded over time from earlier versions (which had fewer, like just Process, File, Interprocess). Some classes cover core ES events, while others include macOS-specific behaviors or enrichments.
Here’s a breakdown in a table for clarity:
| Event Class | Description | Key Events/Examples Included | Use Cases for Security/Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process | Core process lifecycle events | NOTIFY_EXEC, NOTIFY_FORK, NOTIFY_EXIT, process args/env vars | Detecting new process launches, command-line activity, malware execution |
| Interprocess | Communication/coordination between processes | Signals, remote thread creation, task port access | Spotting process injection or debugging attempts |
| File system | Basic file operations | CREATE, OPEN, WRITE, CLOSE, RENAME, DELETE/UNLINK | Tracking file drops, modifications, ransomware patterns |
| File metadata | Changes to file attributes and extended info | SETATTRLIST, SETEXTATTR, SETFLAGS, SETMODE, SETOWNER, time changes | Detecting timestamp stomping or metadata tampering |
| File system mounting | Mounting/unmounting volumes | MOUNT, UNMOUNT, REMOUNT | Monitoring external drives or filesystem changes |
| Code signing | Code signature validation and invalidation | CS_INVALIDATED, CODE_SIGNATURE_VALIDATED | Identifying tampered or unsigned binaries |
| Gatekeeper | Apple’s app execution policy enforcement | Related to quarantine checks and validation (enriched from signing events) | Spotting blocked/ad-hoc app runs |
| XProtect | Apple’s built-in malware scanner detections | Enrichments from scans/remediations (e.g., YARA signature hits) | Detecting known threats via Apple’s engine |
| Kernel | Kernel-level extensions and low-level ops | KEXTLOAD, KEXTUNLOAD (rare now due to deprecation) | Monitoring legacy kernel code loads |
| Login | User login/logout events | Login-related hooks (e.g., session creation) | Tracking user sessions or login items |
| MDM | Mobile Device Management profile changes | MDM enrollment or command events | Enterprise monitoring for managed devices |
| Memory mapping | Memory allocation and protection changes | MMAP, MPROTECT | Detecting code injection or shellcode execution (e.g., RWX pages) |
| OpenSSH | SSH-specific activities | SSH key access or connection events | Monitoring remote access attempts |
| Socket | Network socket operations | BIND, CONNECT, LISTEN | Tracking outbound/inbound connections (potential C2) |
| Authorization | Authorization checks (e.g., auth/open events) | Various AUTH_ events (observable in notify mode) | Seeing privilege escalations or denied actions |
| Service Management | Launchd/daemon/agent management | BTM_LAUNCH_ITEM_ADD (Background Task Management) | Detecting persistence via LaunchAgents/Daemons |
| Link | Hard/soft link creation and resolution | LINK, READLINK, symlink ops | Tracking persistence or evasion via links |
| TCC | Transparency, Consent, and Control (privacy permissions) | TCC_MODIFY (newer macOS) – changes to privacy grants | Detecting malware requesting camera/mic/screen access |
| Task port | Access to Mach task ports | GET_TASK, GET_TASK_READ | Preventing/spotting process introspection or injection |
| XPC | XPC inter-process communication | XPC_CONNECT, service creation | Monitoring app-to-app or app-to-system communication (mac-monitor uses this itself!) |
| Directory | Directory enumeration and lookups | READDIR, LOOKUP | Recon activity like scanning folders |
| File Provider | Cloud/sync provider interactions (e.g., iCloud) | FILE_PROVIDER_MATERIALIZE, FILE_PROVIDER_UPDATE | Tracking cloud file access/modifications |
| UID/GID | User/group ID changes | SETUID, SETEUID, SETGID | Detecting privilege escalation (e.g., setuid binaries) |
| Clock | System time changes | SETTIME | Spotting time manipulation for evasion |
Tips:
- In the app, you can expand each class to toggle individual events for finer control.
- Start with a few classes (e.g., Process + File system + Memory mapping) to avoid overwhelming telemetry.
- Recent versions (post-2025) standardized these to match tools like eslogger for compatibility.
Endpoint Security Framework (ES) Event Types
Apple’s Endpoint Security Framework defines many event types in the es_event_type_t enum. These split into AUTH (authorizable – ES clients can allow/deny before the action) and NOTIFY (notification-only – observe after or during the action).
Below are comprehensive tables based on the latest Apple documentation (as of early 2026), including events up to macOS 15.x. A notable addition in macOS 15.4 is ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_TCC_MODIFY for monitoring Transparency, Consent, and Control (TCC) privacy permission changes.
Events provide rich data via specific structs (e.g., es_event_exec_t includes process details, arguments, environment variables, code signing info). In tools like mac-monitor, NOTIFY events are primarily used for observation, enrichment, and correlation.
I’ve grouped them into two tables for readability. Use cases focus on security research, malware analysis, and troubleshooting (relevant to mac-monitor).
Authorization Events (AUTH) – Can Be Allowed/Denied
These allow potential blocking (e.g., in EDR tools).
| Event Constant | Description | Key Data Provided | Security/Monitoring Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_CHDIR | Change working directory | Target path, process | Detect navigation to suspicious directories |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_CHROOT | Change root directory | New root path | Spot containment escapes or jailbreaks |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_CLONE | Clone a file | Source/target files | Monitor file duplication for persistence |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_COPYFILE | Copy a file | Source/target | Track data exfiltration attempts |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_CREATE | Create a file | Path, mode | Detect new malware drops or persistence files |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_DELETEEXTATTR | Delete extended attribute | File, attribute name | Monitor tampering with quarantine/metadata |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_EXCHANGEDATA | Exchange data between files | Two file paths | Detect atomic file swaps (common in malware) |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_EXEC | Execute a binary | Target executable, args, signing info | Block/prevent malicious executions |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_FCNTL | File control operations | File descriptor, command | Monitor lock acquisitions or flags |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_FILE_PROVIDER_MATERIALIZE | File provider materialize | File reference | Cloud sync monitoring |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_FILE_PROVIDER_UPDATE | File provider update | Updated file | Detect cloud-based modifications |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_FSGETPATH | Get filesystem path | File reference | Track path resolutions |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_GET_TASK | Get task control port | Target process | Prevent process injection/debugging |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_GET_TASK_READ | Get task read port | Target process | Similar to above, read-only access |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_GETATTRLIST | Get file attributes | File, attribute list | Monitor attribute queries |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_GETEXTATTR | Get extended attribute | File, attribute | Quarantine or metadata checks |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_IOKIT_OPEN | Open IOKit device | Device class, user client type | Block hardware access (e.g., keyloggers) |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_KEXTLOAD | Load kernel extension | KEXT path | Prevent unauthorized kernel code (rare now) |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_LINK | Create hard link | Source/target | Detect persistence via links |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_LISTEXTATTR | List extended attributes | File | Metadata enumeration |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_MMAP | Map file into memory | File, protection flags | Detect code injection via mappings |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_MOUNT | Mount filesystem | Mount point | Block unauthorized mounts |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_MPROTECT | Change memory protection | Address, protection | Detect RWX memory for shellcode |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_OPEN | Open a file | Path, flags (read/write/etc.) | Control sensitive file access |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_PROC_CHECK | Check process info | Target PID, flavor | Prevent process enumeration |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_PROC_SUSPEND_RESUME | Suspend/resume process sockets | Target process | Network disruption attempts |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_READDIR | Read directory | Directory path | Directory scanning for recon |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_READLINK | Read symlink | Symlink path | Track symlink resolutions |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_REMOUNT | Remount filesystem | Mount point, flags | Filesystem tampering |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_RENAME | Rename file | Source/target paths | Detect overwrite techniques (e.g., ransomware) |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SEARCHFS | Search filesystem | Volume | Volume searches |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SETACL | Set ACL | File, ACL | Permission escalations |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SETATTRLIST | Set attributes | File, attributes | Metadata changes |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SETEXTATTR | Set extended attribute | File, attribute | Quarantine bypassing |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SETFLAGS | Set file flags | File, flags | Immutable/append-only changes |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SETMODE | Set file mode | File, mode | Permission changes |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SETOWNER | Set file owner | File, owner | Ownership escalations |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SETTIME | Set system time | New time | Detect time stomping |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_SIGNAL | Send signal | Target process, signal | Process termination attempts |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_TRUNCATE | Truncate file | File | Data destruction |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_UIPC_BIND | Bind UNIX socket | Socket path | Local IPC setup |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_UIPC_CONNECT | Connect UNIX socket | Socket | Local communication |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_UNLINK | Delete file | Path | Prevent file deletions |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_AUTH_UTIMES | Change file times | File, times | Timestamp manipulation |
Notification Events (NOTIFY) – Observation Only
These are post-action or during-action notifications (most common in mac-monitor).
| Event Constant | Description | Key Data Provided | Security/Monitoring Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_ACCESS | Check file access | File, mode | Permission probes |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_CHDIR | Change directory | Path | Navigation tracking |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_CHROOT | Change root | Path | Containment changes |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_CLONE | Clone file | Files | Duplication tracking |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_CLOSE | Close file | File descriptor, modified flag | File session end |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_COPYFILE | Copy file | Source/target | Data copying |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_CREATE | Create file | Path | New file drops (malware/persistence) |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_CS_INVALIDATED | Code signature invalidated | Process | Tampering detection |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_DELETEEXTATTR | Delete extended attr | File, attr | Metadata removal |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_DUP | Duplicate FD | FD | Handle passing |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_EXCHANGEDATA | Exchange file data | Files | Atomic swaps |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_EXEC | Execute binary | Process, args, env, signing | Process launches (core for malware detection) |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_EXIT | Process exit | Process, exit code | Process termination |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_FCNTL | File control | FD, command | Locks/flags |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_FILE_PROVIDER_MATERIALIZE | Materialize file | File | Cloud file access |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_FILE_PROVIDER_UPDATE | Update file | File | Cloud modifications |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_FORK | Fork process | Child process | Process creation |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_FSGETPATH | Get path | Path | Path resolution |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_GETATTRLIST | Get attributes | File | Attribute reads |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_GETEXTATTR | Get extended attr | File, attr | Quarantine checks |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_GET_TASK* | Get task ports | Target process | Debugging/injection |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_IOKIT_OPEN | Open IOKit | Device | Hardware interaction |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_KEXTLOAD/UNLOAD | Load/unload KEXT | KEXT path | Kernel changes (deprecated) |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_LINK | Create hard link | Files | Persistence |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_LISTEXTATTR | List extended attrs | File | Metadata enum |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_LOOKUP | Path lookup | Path | Recon |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_MMAP | Map memory | File, flags | Injection detection |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_MOUNT/UNMOUNT | Mount/unmount | Mount point | Filesystem changes |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_MPROTECT | Change memory protection | Address, prot | Shellcode prep |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_OPEN | Open file | Path, flags | File access tracking |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_PTY_* | Pseudoterminal ops | PTY device | Interactive shells |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_READDIR | Read directory | Dir | Directory enumeration |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_READLINK | Read symlink | Symlink | Symlink tracking |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_REMOTE_THREAD_CREATE | Create remote thread | Target process | Injection |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_REMOUNT | Remount | Mount | Filesystem flags |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_RENAME | Rename | Source/target | Overwrite/ransomware |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_SET* (ACL, ATTR, EXTATTR, FLAGS, MODE, OWNER, TIME, etc.) | Set various attributes | File, new values | Permission/metadata changes |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_SETEUID/SETUID etc. | Privilege changes | New IDs | Escalation detection |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_SIGNAL | Send signal | Target, signal | Kill attempts |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_STAT | Stat file | File | File info queries |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_TRACE | Trace process | Target | Debugging |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_TRUNCATE | Truncate file | File | Data wipe |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_UIPC_* | UNIX socket ops | Socket | Local IPC |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_UNLINK | Delete file | Path | Deletion tracking |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_WRITE | Write to file | File | Modification/ransomware |
| ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_TCC_MODIFY (macOS 15.4+) | TCC permission modify | Service, identity, right, reason | Detect privacy grants (e.g., malware getting Accessibility) |
This covers the core set; some niche events (e.g., XPC connect, launch items) may exist in specific macOS versions but aren’t universally listed. In mac-monitor, toggle these in the UI to reduce noise – start with EXEC, FORK, EXIT, CREATE, OPEN, WRITE, RENAME, UNLINK for basic monitoring.
- https://developer.apple.com/documentation/endpointsecurity/es_event_type_t
- https://www.huntress.com/blog/endpoint-security-in-a-macos-world
- https://developer.apple.com/documentation/endpointsecurity/event-types
- https://objective-see.org/blog/blog_0x7F.html
- https://gist.github.com/Omar-Ikram/8e6721d8e83a3da69b31d4c2612a68ba
- https://www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/collecting-telemetry-data-on-macos-using-endpoint-security
- https://www.elastic.co/blog/mac-system-extensions-for-threat-detection-part-3
Guided Walkthrough of Mac Monitor: Step-by-Step Usage with Explanations and Real-World Examples
- Upon launch, Mac Monitor establishes an XPC connection to its System Extension, which subscribes to ES events. This extension remains dormant until a trace is started, minimizing resource usage. The app’s interface will appear as a clean window with a toolbar at the top, a central table for event display, and a left sidebar for process trees.
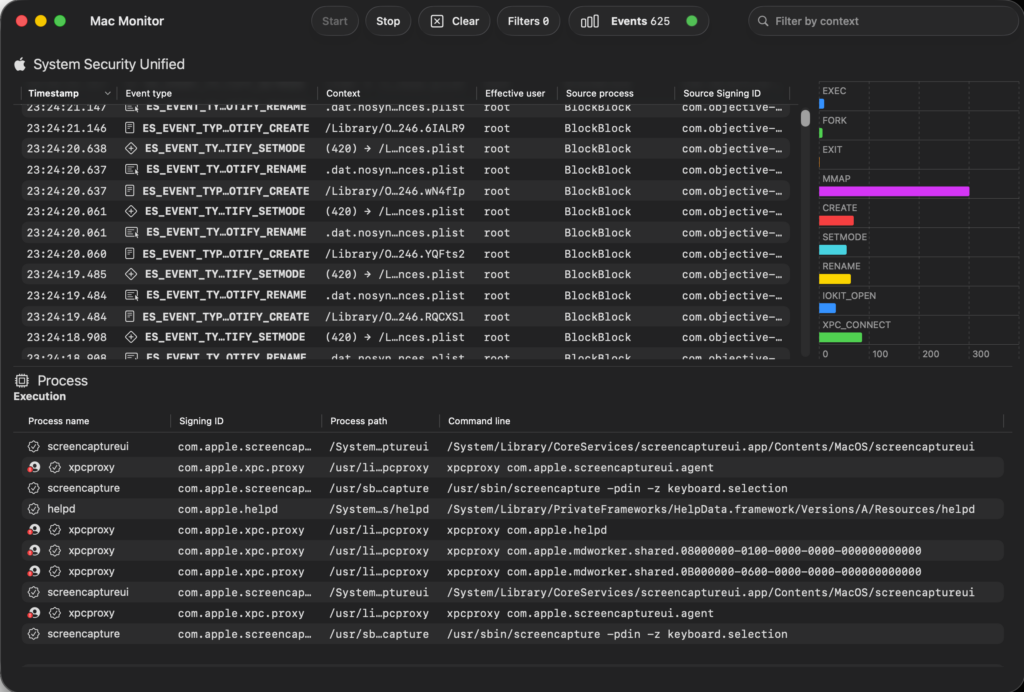
- Click the “Start” button in the toolbar. Events will begin populating the table in real-time. This activates the System Extension to subscribe to ES event types, such as process creations (ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_FORK and ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_EXEC), file operations (ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_WRITE), or memory mappings (ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_MMAP). Events are enriched with metadata like code signing certificates, environment variables, and quarantine status (e.g., for downloaded files).
- You may see a flood of system events from background processes. This is normal; macOS generates thousands of events per minute. To manage noise, proceed to filtering in later steps.
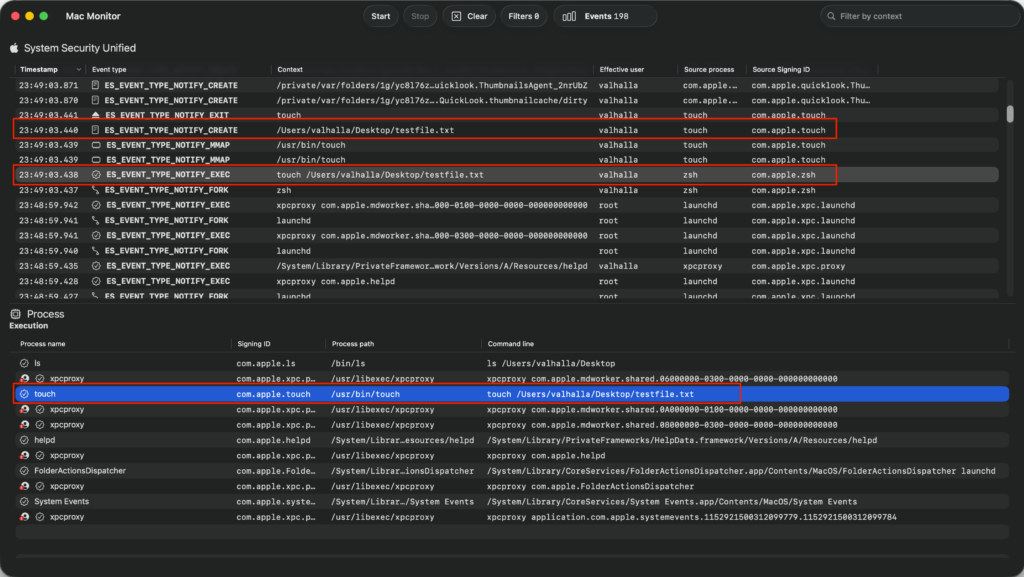
Real-World Example 1: Monitoring Basic File Operations via Terminal
Simulate a simple file creation and access, common in debugging or detecting unauthorized modifications.
- Open Terminal.app (or any shell).
- Run: touch ~/Desktop/testfile.txt (creates an empty file).
- Then: echo “Hello, world” > ~/Desktop/testfile.txt (writes content).
- Finally: ls ~/Desktop (lists directory contents).
Expected in Mac Monitor:
- Look for ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_CREATE for the touch command, showing the initiating process as /bin/zsh (or your shell) and target path /Users/<yourusername>/Desktop/testfile.txt.
- The echo triggers ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_WRITE, enriched with metadata like file permissions and no quarantine (since it’s locally created).
- ls generates ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY_EXEC or ES_EVENT_TYPE_NOTIFY for directory reads.
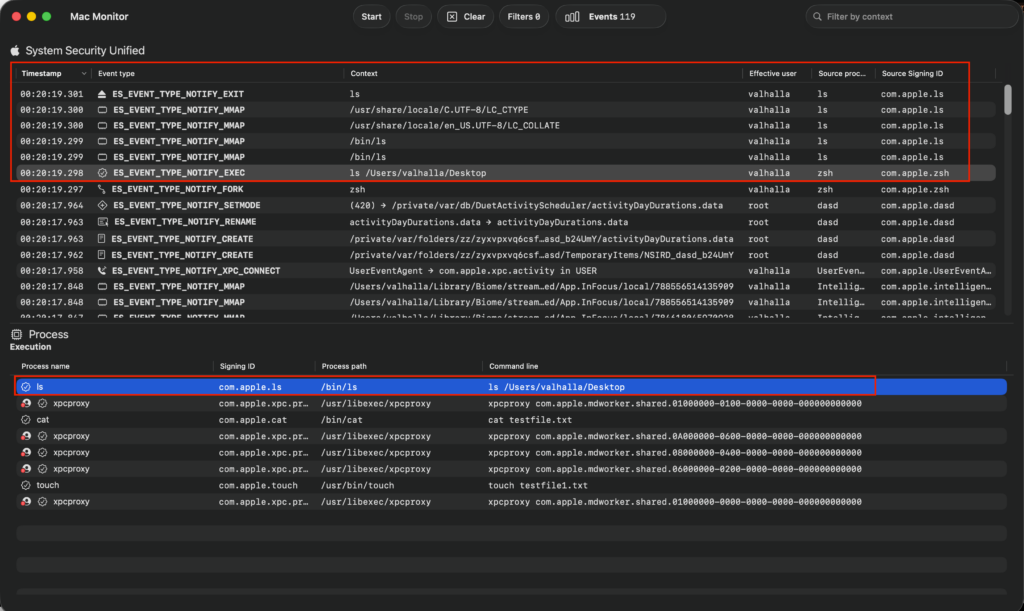
This example mirrors real-world threat hunting, where monitoring file writes could detect ransomware encrypting documents.
Real-World Example 2: Monitoring a Network Download and Process Execution
Emulate downloading and running a script, useful for analyzing potential malware or app behaviors.
- Run: curl -O http://malware.wicar.org/data/eicar.com (downloads a file; replace with a safe URL).
- Then: chmod +x eicar.com (makes it executable).

